Automating Everything
To conclude, we will see how all these steps can be automated with GitHub Actions.
A GitHub action (or "workflow") is a series of tasks that can be automated to run at a certain time, e.g. on each pull request or merge to your GitHub repo. Actions are specified with YAML config files. Let's build ours up piece by piece.
First, create the YAML config file.
mkdir -p .github/workflows && touch .github/workflows/build.yml
We will start by adding a name and defining when our action will run.
name: build
on:
push:
branches: [ master ]
pull_request:
branches: [ master ]
This says that our job, named build, will run on every push and pull request to the master branch of our repository. Next, we define the "build matrix".
name: build
on:
push:
branches: [ master ]
pull_request:
branches: [ master ]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
strategy:
matrix:
os: [windows-latest, ubuntu-latest, macos-latest]
python-version: [3.6, 3.7, 3.8]
This means that our action steps will run independently for each of the latest available versions of the Windows, Ubuntu and macOS operating systems on Python versions 3.6, 3.7, and 3.8. Finally, we add the steps to our workflow.
Check out our Repository and Set up python
These built-in actions will checkout out our repository and set up the appropriate Python version.
name: build
on:
push:
branches: [ master ]
pull_request:
branches: [ master ]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
strategy:
matrix:
os: [windows-latest, ubuntu-latest, macos-latest]
python-version: [3.6, 3.7, 3.8]
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
uses: actions/setup-python@v2.1.1
with:
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
Install our Package with Poetry
Using a third-party action, we will install our package with Poetry.
name: build
on:
push:
branches: [ master ]
pull_request:
branches: [ master ]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
strategy:
matrix:
os: [windows-latest, ubuntu-latest, macos-latest]
python-version: [3.6, 3.7, 3.8]
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
uses: actions/setup-python@v2.1.1
with:
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
- name: Install Poetry
uses: abatilo/actions-poetry@v2.0.0
- name: Install dependencies with Poetry
run: |
poetry install
Lint and Format our Code
Next, we will lint and format our code with flake8 and black, just like we did locally.
name: build
on:
push:
branches: [ master ]
pull_request:
branches: [ master ]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
strategy:
matrix:
os: [windows-latest, ubuntu-latest, macos-latest]
python-version: [3.6, 3.7, 3.8]
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
uses: actions/setup-python@v2.1.1
with:
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
- name: Install Poetry
uses: abatilo/actions-poetry@v2.0.0
- name: Install dependencies with Poetry
run: |
poetry install
- name: Format code with black
run: |
poetry run black .
- name: Lint with flake8
run: |
# stop the build if there are Python syntax errors or undefined names
poetry run flake8 . --count --select=E9,F63,F7,F82 --show-source --statistics
# exit-zero treats all errors as warnings.
poetry run flake8 . --count --exit-zero --max-complexity=10 --statistics
Test out Code
Finally, we will run our tests using pytest.
name: build
on:
push:
branches: [ master ]
pull_request:
branches: [ master ]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
strategy:
matrix:
os: [ubuntu-latest, macos-latest]
python-version: [3.6, 3.7, 3.8]
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
uses: actions/setup-python@v2.1.1
with:
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
- name: Install Poetry
uses: abatilo/actions-poetry@v2.0.0
- name: Install dependencies with Poetry
run: |
poetry install
- name: Format code with black
run: |
poetry run black .
- name: Lint with flake8
run: |
# stop the build if there are Python syntax errors or undefined names
poetry run flake8 . --count --select=E9,F63,F7,F82 --show-source --statistics
# exit-zero treats all errors as warnings.
poetry run flake8 . --count --exit-zero --max-complexity=10 --statistics
- name: Test with pytest
run: |
poetry run pytest tests
Now, every time we open a pull request or push our code to master, everything we have discussed in this guide will run automatically. If any of the individual steps fail, the build will fail. Otherwise, the build will pass.
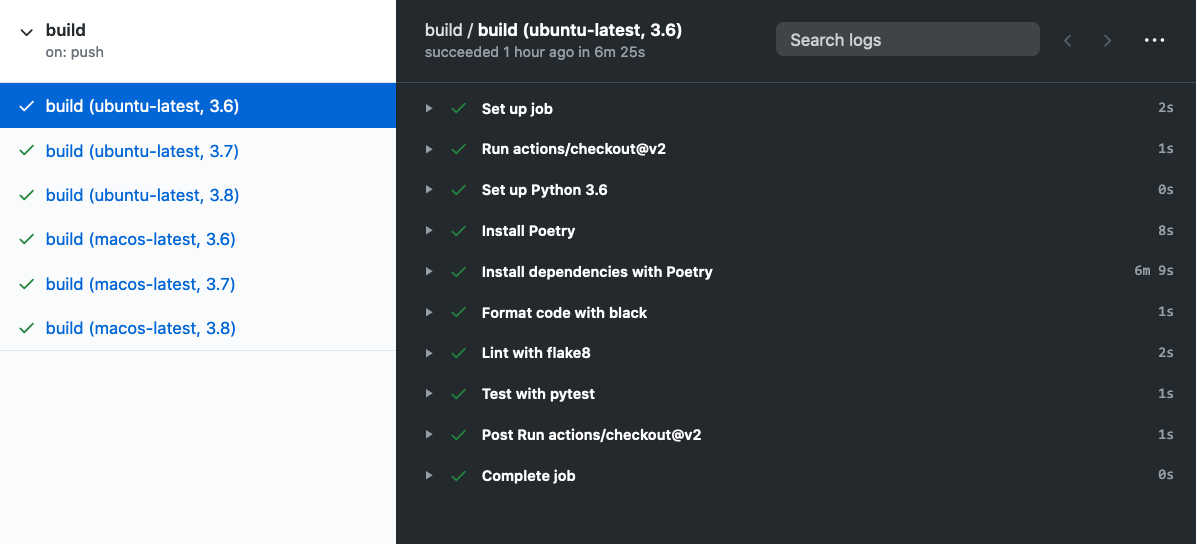
For example, the build status of the repository where this guide lives is:
Thats the end of the guide! We covered some of the most important best practices in software engineering, and specific tools to automate each of them. Then, we learned how we can automate an entire build using GitHub Actions. Checkout the GitHub repository where this guide lives for all the code we covered in the guide.